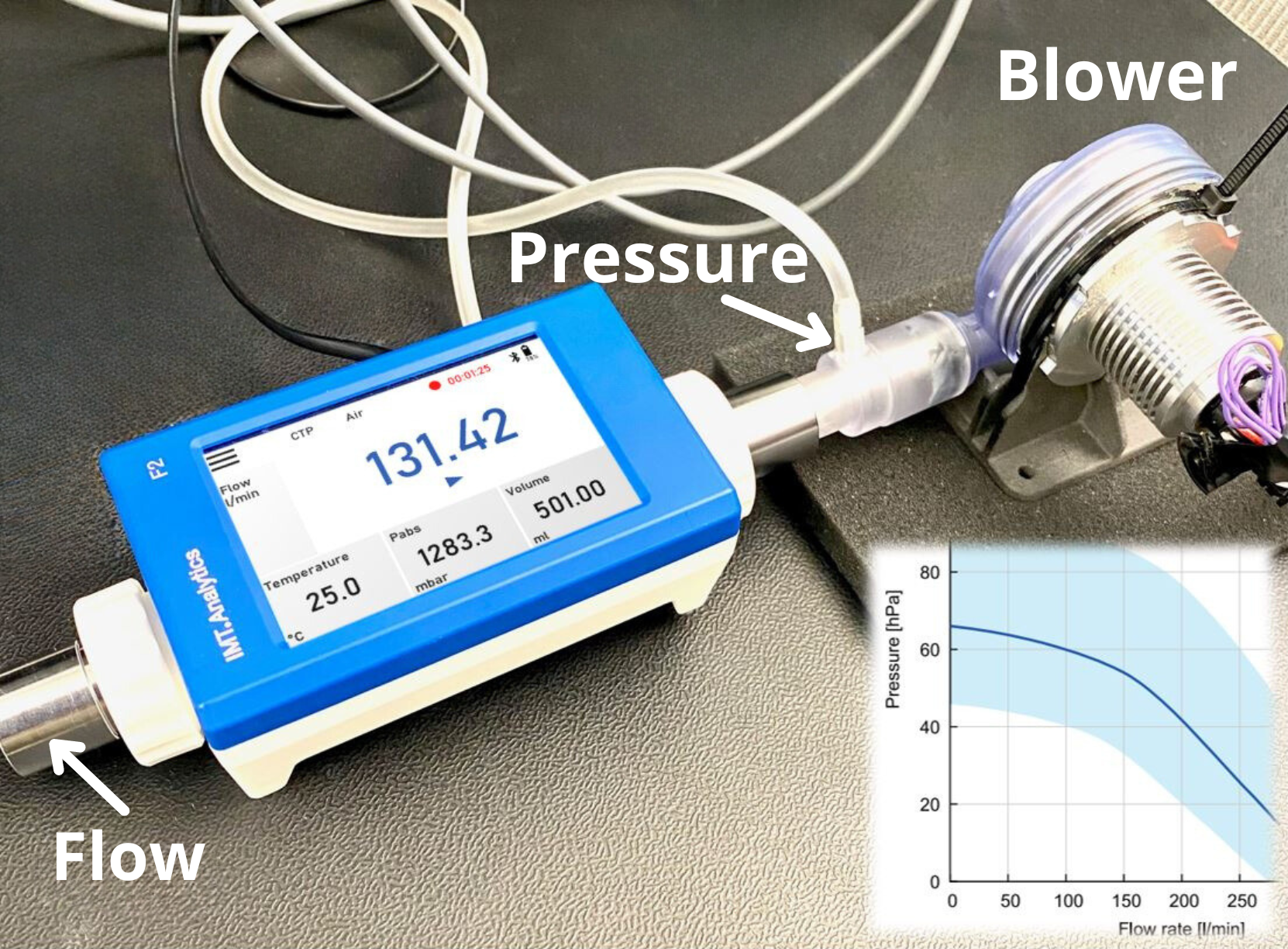
Introduction:
In the realm of medical devices, ventilators play a critical role in providing respiratory support to patients in need. To ensure the quality, reliability, and safety of these life-saving devices, specific guidance regarding ventilator testing has been established. In this article, we will delve into the importance of ventilator testing and explore the key elements of the guidance provided by regulatory bodies and standards organizations.
The Regulatory Framework:
The regulatory framework governing medical devices, including ventilators, provides guidance for manufacturers to ensure compliance with quality and safety standards. While specific regulations may vary across countries, we will focus on the guidance provided by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
21 CFR Part 820 – Quality System Regulations: Under the FDA’s Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), 21 CFR Part 820 sets forth quality system regulations for medical devices. While it does not outline detailed ventilator testing procedures, it provides a framework for manufacturers to establish quality management systems and implement appropriate testing and validation activities. This includes design controls, production and process controls, and calibration and maintenance of inspection and test equipment.
Standards and Guidelines:
In addition to regulatory requirements, recognized standards and guidelines provide further guidance on ventilator testing. These standards are developed by organizations such as the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
- AAMI/ISO 80601-2-12 – Requirements for Basic Safety and Essential Performance of Critical Care Ventilators: This standard specifically addresses the safety and essential performance requirements for critical care ventilators. It outlines testing and verification procedures to ensure compliance with essential performance parameters, such as ventilation accuracy, alarms, and monitoring capabilities. It also covers electrical safety, mechanical performance, and environmental requirements.
- AAMI/ISO 18562 – Biocompatibility Evaluation of Breathing Gas Pathways in Healthcare Applications: This standard focuses on the biocompatibility evaluation of breathing gas pathways, including components used in ventilators. It provides guidance on testing the compatibility of materials and potential risks associated with patient contact.
The Importance of Ventilator Testing:
Ventilator testing is crucial to verify that these devices meet the required performance, safety, and reliability standards. It helps identify potential issues, validate functionality, and ensure appropriate settings and alarms. Key areas of ventilator testing include:
- Performance Verification:
- Ventilation accuracy: Assessing the device’s ability to deliver accurate tidal volume, respiratory rate, and inspiratory/expiratory times.
- Alarms: Verifying proper alarm functionality and audibility under various conditions.
- Monitoring capabilities: Testing the accuracy and reliability of monitoring parameters like oxygen concentration, pressure, and flow.
- Safety and Compliance Checks:
- Electrical safety: Evaluating insulation integrity, leakage currents, and grounding.
- Mechanical safety: Assessing the device’s structural integrity, moving parts, and potential hazards.
- Biocompatibility: Ensuring materials used in breathing gas pathways are compatible with human tissue and pose no undue risks.
Implementing Ventilator Testing: Manufacturers play a vital role in conducting comprehensive testing during the development and manufacturing phases of ventilators. They follow the specific guidance outlined by regulatory bodies and standards organizations to ensure compliance and safety.
Furthermore, healthcare facilities and biomedical engineering departments perform routine testing and maintenance to ensure ongoing device performance and safety. This includes functional checks, calibration, and verification of alarms, sensors, and monitoring parameters.
Conclusion:
Ventilator testing is a critical process to ensure the quality, safety, and reliability of these life-supporting devices. By adhering to the specific guidance provided by regulatory bodies and standards organizations, manufacturers and healthcare facilities can